Black widow spiders belong to the Latrodectus genus and are famous for their potent venom and the female’s iconic red hourglass marking. While most people are familiar with the Southern Black Widow, there are actually many different types found across the world—from North America to Africa, Asia, and the Mediterranean. Each species has its own unique traits, preferred habitats, and bite risks. In this guide, you’ll find details about 15 black widow species, how to identify them, where they live, and what to know about their bites.
1. Southern Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans)
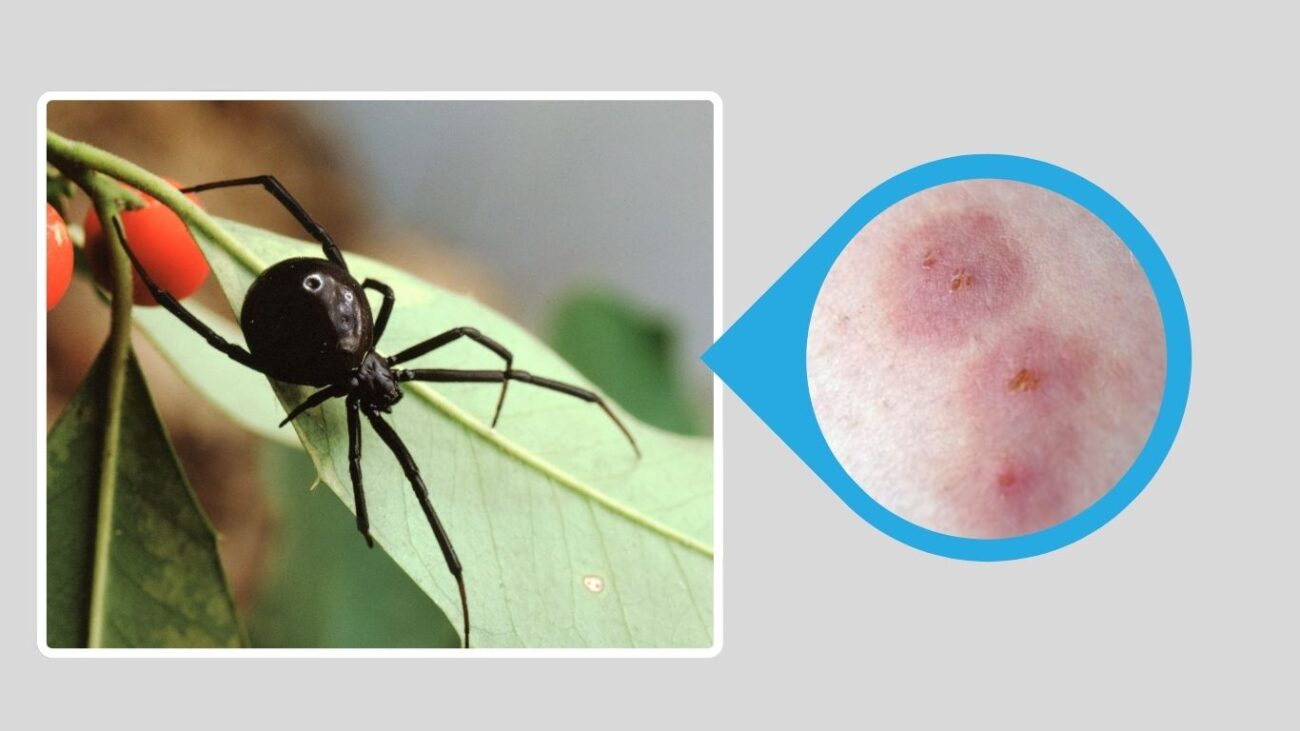

The Southern Black Widow is one of the most easily recognized spiders in North America due to its glossy black body and bright red hourglass marking on the underside of its abdomen. Despite its dangerous reputation, it is a shy spider that only bites when disturbed.
Identification
- Glossy black body
- Red hourglass marking on the underside of the abdomen
- Female size up to 1.5 inches including leg span
- Males are smaller and duller in color
- Smooth, rounded abdomen
Habitat
Southern Black Widows prefer dark, undisturbed environments. They are commonly found in garages, basements, outdoor sheds, under rocks, inside woodpiles, and in cluttered corners. Their webs are irregular, messy, and typically built close to the ground.
Bite
Only the female bites humans, usually in self-defense. The venom is neurotoxic and can cause sharp pain, abdominal cramping, nausea, and sweating. Although the symptoms can be severe, fatalities are extremely rare, and most healthy adults recover fully with prompt medical care.
Is the Southern Black Widow deadly?
No, the bite is rarely fatal. It can cause intense discomfort, but with medical treatment, most people recover without serious complications.
Where do Southern Black Widows usually hide?
They hide in dark, quiet, and sheltered areas such as woodpiles, outdoor storage, under rocks, and inside cluttered buildings where they are less likely to be disturbed.
How can you treat a Southern Black Widow bite?
First aid includes cleaning the bite, applying ice to reduce swelling, and keeping the affected area elevated. It’s important to seek medical help, especially if symptoms worsen. Antivenom may be used in serious cases.
2. Western Black Widow (Latrodectus hesperus)
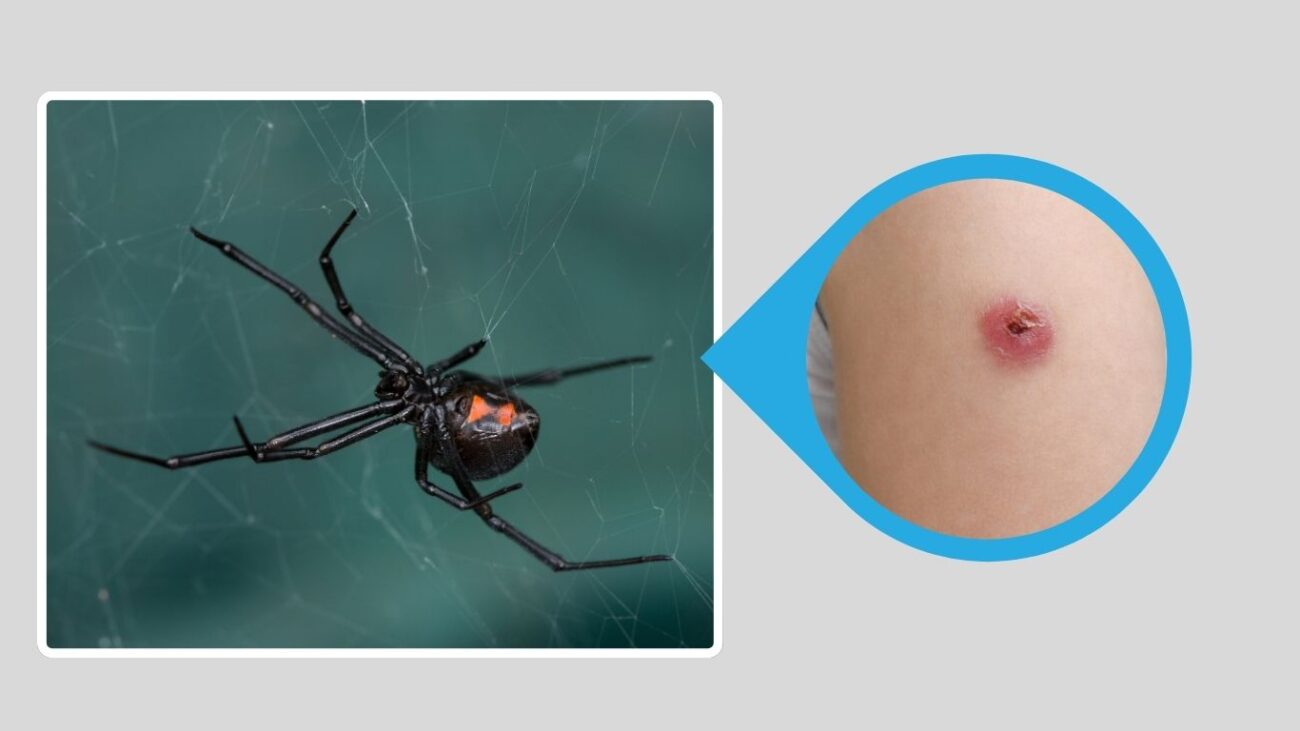
The Western Black Widow is native to the western United States and is nearly identical in appearance to the Southern Black Widow. It is most active during warm months and commonly found in dry, sheltered outdoor areas. Like its southern relative, it poses a threat mainly through the female’s venomous bite.
Identification
- Glossy black body
- Red or orange hourglass on the underside of the abdomen
- Female size up to 1.5 inches
- Males are smaller and lighter brown
- Round, bulbous abdomen
Habitat
Western Black Widows prefer dry, protected spaces such as rock piles, woodpiles, crawlspaces, and wall voids. They build messy webs in low, hidden spots where insects are likely to pass by.
Bite
The venom can cause localized pain, cramping, and other systemic symptoms like nausea or sweating. Though serious, the bite is rarely life-threatening, especially with timely medical care.
Is the Western Black Widow aggressive?
No, it is very shy and bites only when directly threatened or trapped against the skin.
What time of year are they most active?
They are most active in late spring through early fall, especially in warmer regions.
What should I do if bitten by a Western Black Widow?
Clean the bite area, apply a cold compress, and seek medical care. Antivenom may be given if symptoms are severe.
3. Northern Black Widow (Latrodectus variolus)
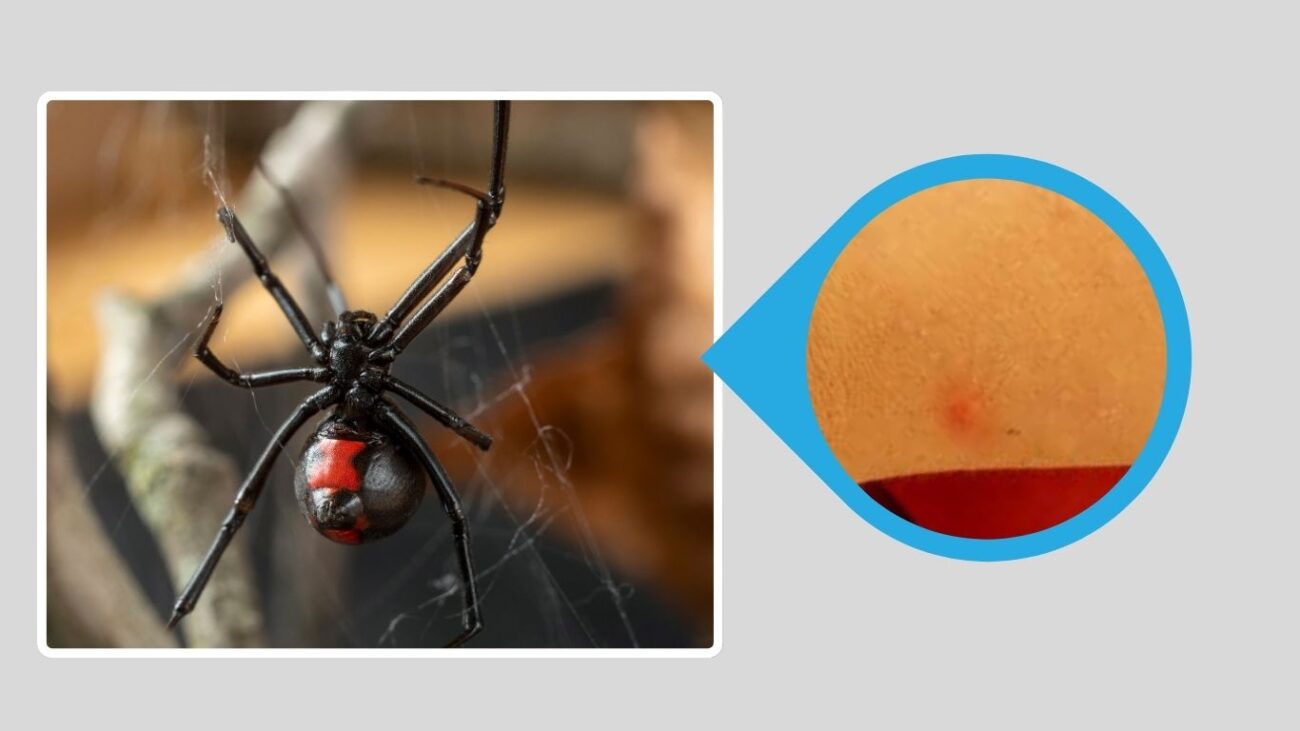

The Northern Black Widow is found mainly in the northeastern and midwestern United States. Unlike the southern and western species, this spider’s hourglass marking is often broken into two red triangles. It is secretive and rarely encountered unless disturbed.
Identification
- Shiny black body
- Red hourglass often broken into two triangles
- May have red spots on top of the abdomen
- Females larger and more vividly marked
- Males smaller, brownish, with lighter markings
Habitat
They live in forests, old stumps, hollow logs, abandoned sheds, and brush piles. They prefer cool, humid environments and stay low to the ground in dark, protected areas.
Bite
The bite can cause pain, muscle rigidity, and nausea. While symptoms may last for several days, they rarely require antivenom unless in vulnerable individuals.
How can I tell a Northern Black Widow from others?
Its hourglass mark is usually broken into two red triangles, and it may also have red or white spots on the back.
Are Northern Black Widows found indoors?
They usually stay outdoors in natural shelters, but may occasionally enter basements or old buildings.
What’s the recovery time after a bite?
Most people recover within a few days with supportive care. Pain relief and rest are typically sufficient.
4. Mediterranean Black Widow (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus)
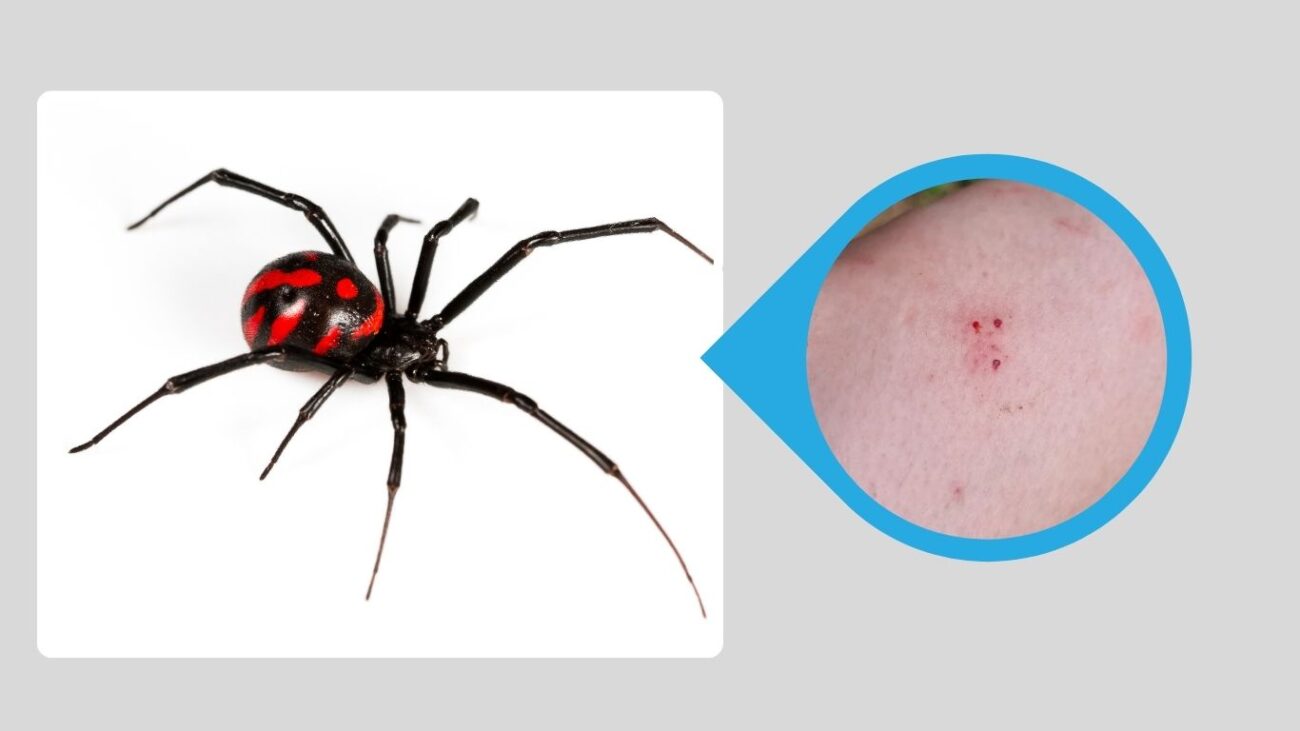

The Mediterranean Black Widow is native to Southern Europe, parts of Asia, and North Africa. It is slightly different in appearance, often displaying red or orange spots on its back. Known locally by various names, it is a medically significant spider due to its potent venom.
Identification
- Shiny black body
- Red or orange spots on the back (usually 13)
- Hourglass mark may be faint or absent
- Females larger with rounded abdomen
- Males smaller and less colorful
Habitat
This spider prefers dry, open areas such as fields, farms, grasslands, and roadside edges. It hides under stones, plant debris, and in cracks near the ground, where it builds irregular webs.
Bite
The bite can cause severe pain, sweating, and muscle cramps. In some cases, it may lead to systemic symptoms, especially in children or the elderly. Hospital treatment is recommended for serious cases.
What does “tredecimguttatus” mean?
It means “thirteen-spotted,” referring to the usual number of red spots found on the spider’s back.
Is the bite more dangerous than other widows?
It’s similar in toxicity to American species, though symptoms can feel stronger due to multiple bites or delayed treatment.
Are Mediterranean Black Widows aggressive?
No, they are shy and typically bite only when handled or pressed against the skin.
5. Brown Widow (Latrodectus geometricus)
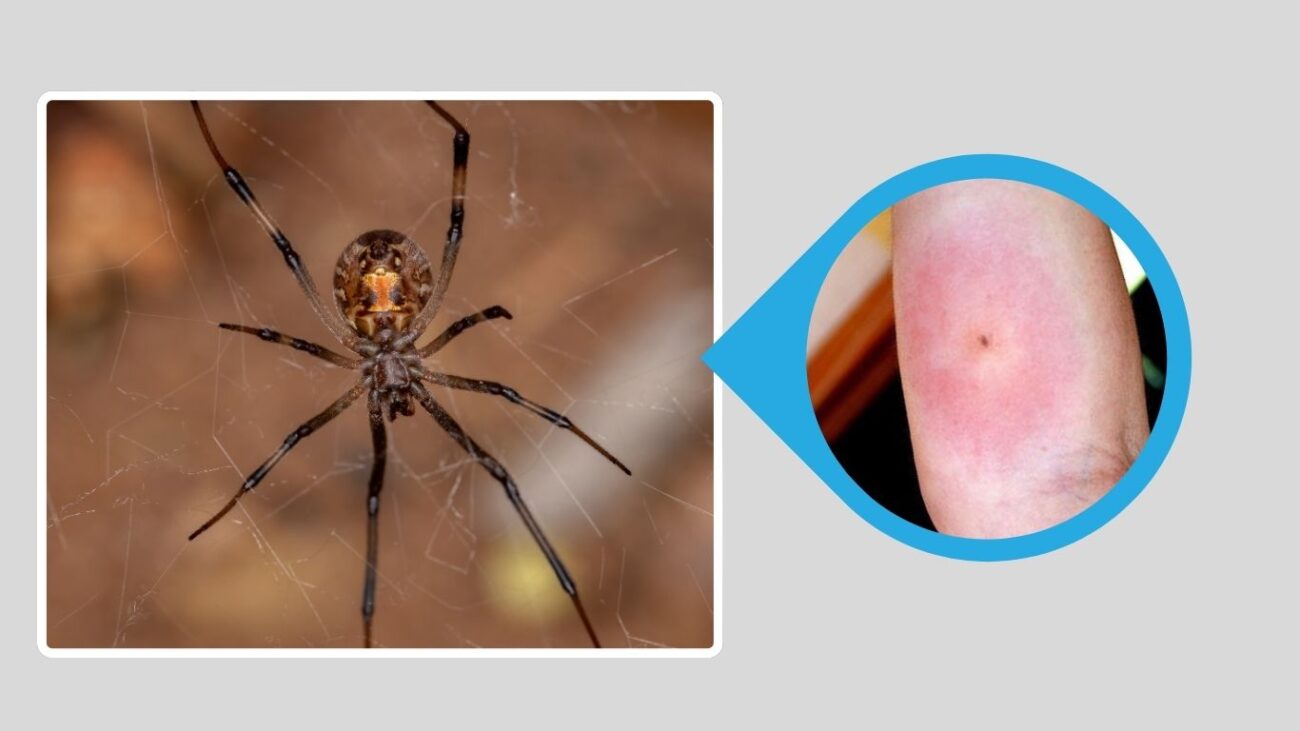
Though not entirely black, the Brown Widow is a close relative of the Black Widow group and shares many behavioral traits. It’s found worldwide and is less toxic than true black widows but still capable of delivering a painful bite.
Identification
- Light brown or tan body
- Orange or yellow hourglass on the underside
- Abdomen has white or dark geometric markings
- Legs may appear banded
- Smaller and less glossy than black widows
Habitat
Brown Widows are often found in urban areas, under outdoor furniture, inside mailboxes, plant pots, and railings. They adapt well to human environments and often outcompete black widows in shared regions.
Bite
The bite is usually less severe than other widow species, causing localized pain and irritation. Systemic effects are rare but can occur in sensitive individuals.
How do Brown Widows differ from Black Widows?
They are lighter in color, have different markings, and are generally less venomous.
Where are Brown Widows found globally?
They are widespread and have been reported in the U.S., Africa, Australia, Japan, and South America.
Should I worry about Brown Widow bites?
Bites are usually mild, but you should still clean the area and monitor symptoms. Seek medical advice if reactions are severe.
6. Caribbean Black Widow (Latrodectus curacaviensis)
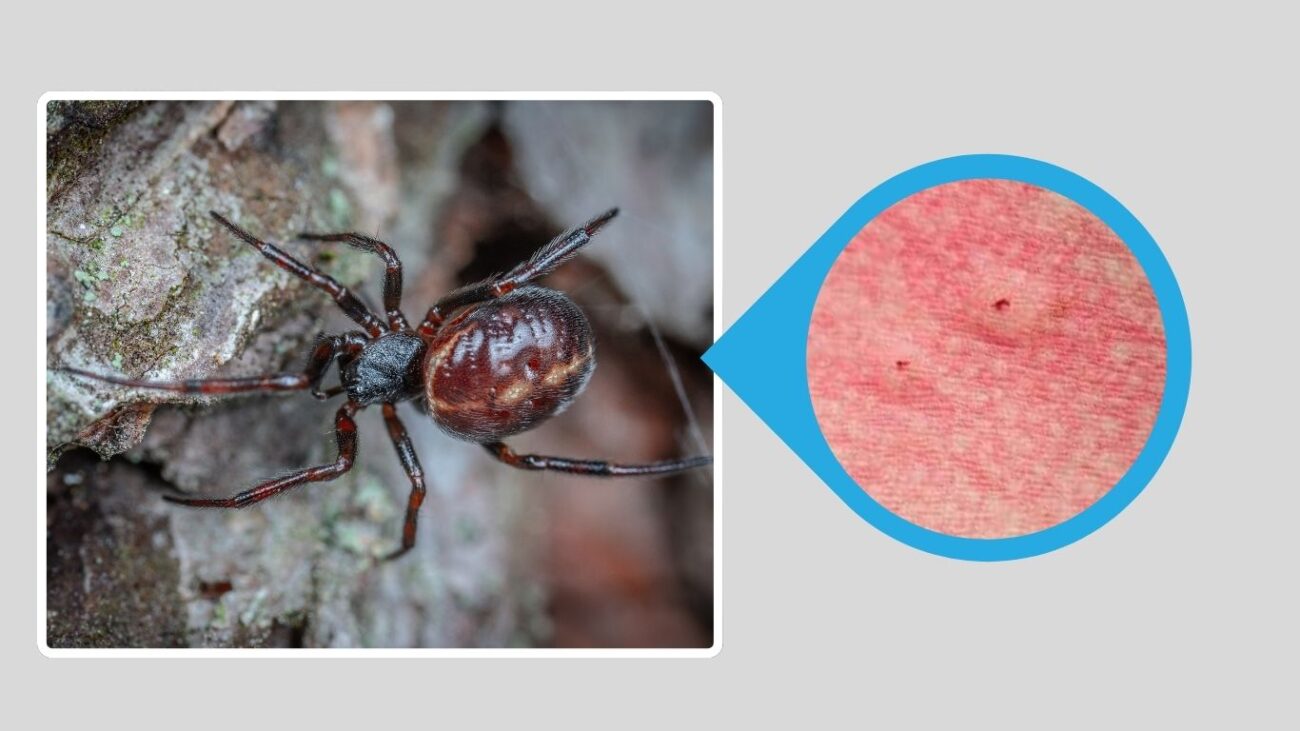
The Caribbean Black Widow is native to the Caribbean region and parts of Central and South America. It shares many characteristics with other widow species but often has slightly varied coloration and markings depending on its exact location.
Identification
- Shiny black body
- Bright red or orange hourglass on the underside
- May have red spots on the top of the abdomen
- Females larger and more striking in color
- Males smaller and less vivid
Habitat
Commonly found in tropical and subtropical environments, including under rocks, logs, abandoned structures, and human-made debris. They thrive in both natural and disturbed habitats.
Bite
The bite delivers neurotoxic venom, causing symptoms like localized pain, muscle cramps, and nausea. While painful, it is rarely life-threatening with prompt care.
What areas are home to the Caribbean Black Widow?
They are mainly found in the Caribbean islands, northern South America, and parts of Central America.
Do they look different from U.S. black widows?
Yes, they sometimes have extra red markings or spots on the back, depending on the region.
Are they a danger to tourists?
Only if disturbed. They’re not aggressive and avoid human contact unless provoked.
7. Southern African Black Widow (Latrodectus indistinctus)
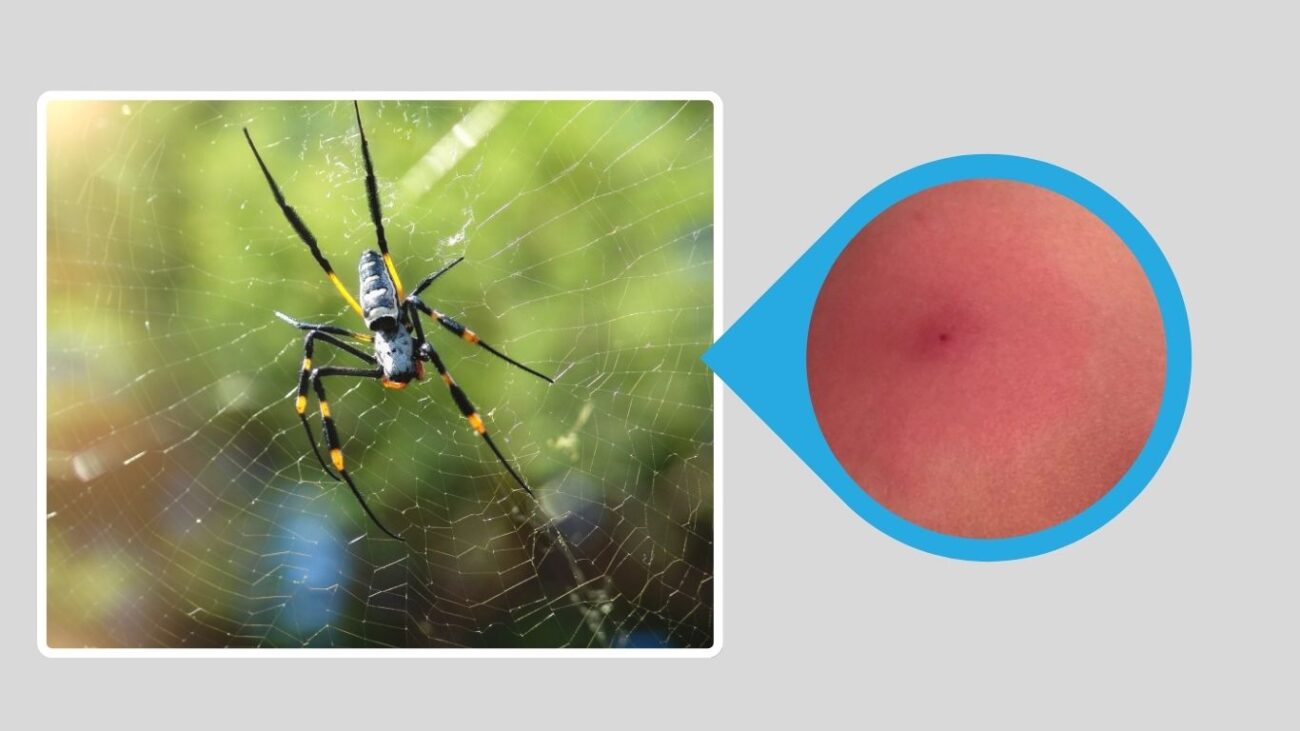
This species is native to southern Africa and is known for its dark, often unmarked appearance. It lives in dry areas and contributes to natural pest control. Like other widow species, the females are more venomous than the males.
Identification
- Matte to glossy black body
- Hourglass may be faint, yellowish, or absent
- Abdomen smooth and rounded
- Females larger and darker
- Males are smaller and paler
Habitat
Found in dry savannas, shrublands, and desert regions. They build irregular webs in rock crevices, termite mounds, and under debris near the ground.
Bite
The venom is potent, leading to sharp pain, tremors, and sweating. Although serious, fatalities are rare with proper medical attention.
Is the Southern African Black Widow easy to identify?
Not always. It lacks the clear hourglass seen in American species, making it harder to spot without close inspection.
Where do they commonly build webs?
In secluded, dry, ground-level areas like rock piles, animal burrows, and under brush.
What should you do if bitten?
Clean the wound, apply ice, and seek medical care. Antivenom may be available in some regions of Africa.
8. Western African Black Widow (Latrodectus cinctus)
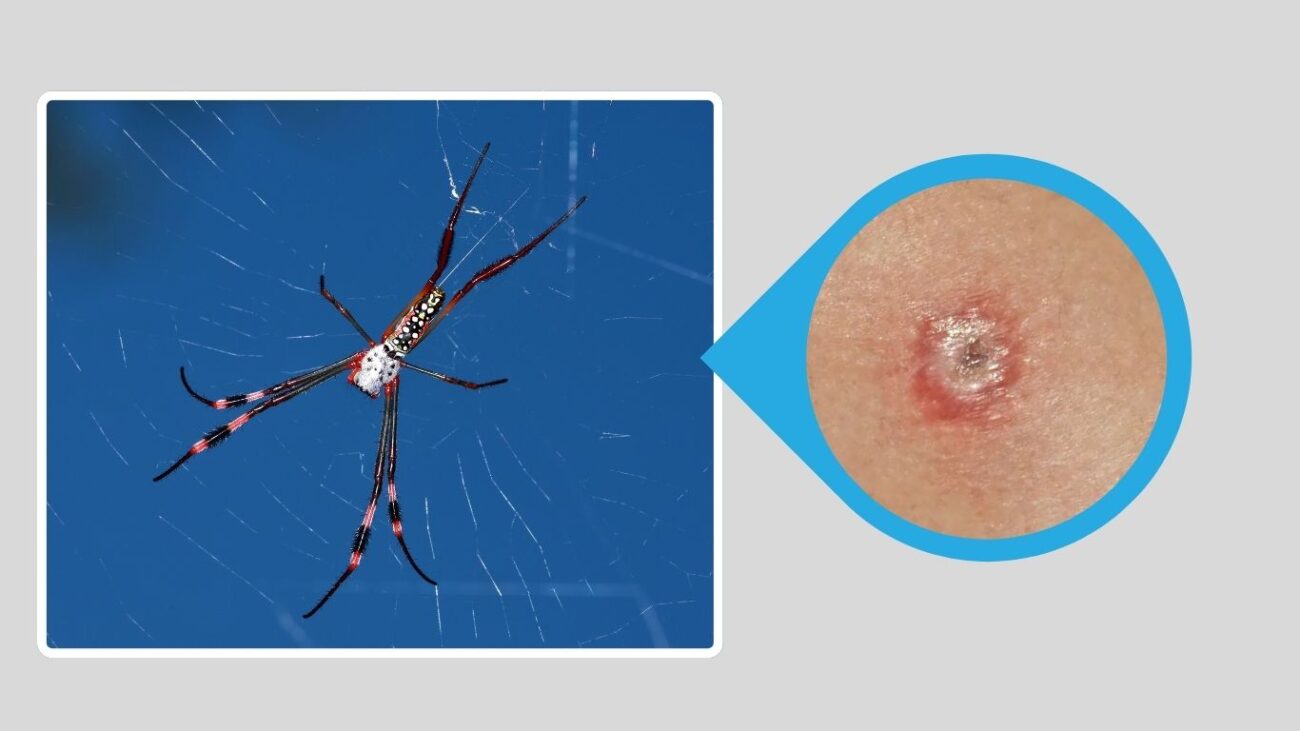
The Western African Black Widow is found across several countries in West and Central Africa. It is less well-known than its American counterparts but poses similar health risks due to its venom. This species can be identified by the presence of colored markings and a generally more robust appearance.
Identification
- Shiny black body with reddish or orange markings
- May have a faded hourglass or lateral spots
- Abdomen rounded and plump
- Females are larger, with stronger contrast in color
- Males are much smaller and typically lighter in tone
Habitat
Latrodectus cinctus prefers hot, dry, and rocky environments. It builds webs in rock crevices, hollow logs, and under loose bark. In rural and semi-urban areas, it may inhabit the corners of animal shelters, old buildings, and piles of construction materials. The webs are irregular and sticky, designed to trap crawling insects.
Bite
Bites from this species are venomous and may cause intense localized pain within an hour. Victims often report abdominal cramping, excessive sweating, tremors, and general weakness. Symptoms may last from 24 to 72 hours, depending on the victim’s age, health, and access to care. While rarely fatal, severe bites require medical treatment, especially in children and the elderly.
What makes this species distinct from others?
Its reddish or orange markings may appear in different patterns—not always in a classic hourglass shape—making identification trickier in the field.
Are their bites more dangerous than American species?
Not necessarily more dangerous, but they can be just as severe. Lack of access to immediate medical care in some areas may increase risks.
How long do symptoms last after a bite?
Symptoms typically subside within 2 to 3 days but may linger longer without medical intervention. Pain relievers, hydration, and muscle relaxants are common treatments.
9. Indian Black Widow (Latrodectus hystrix)
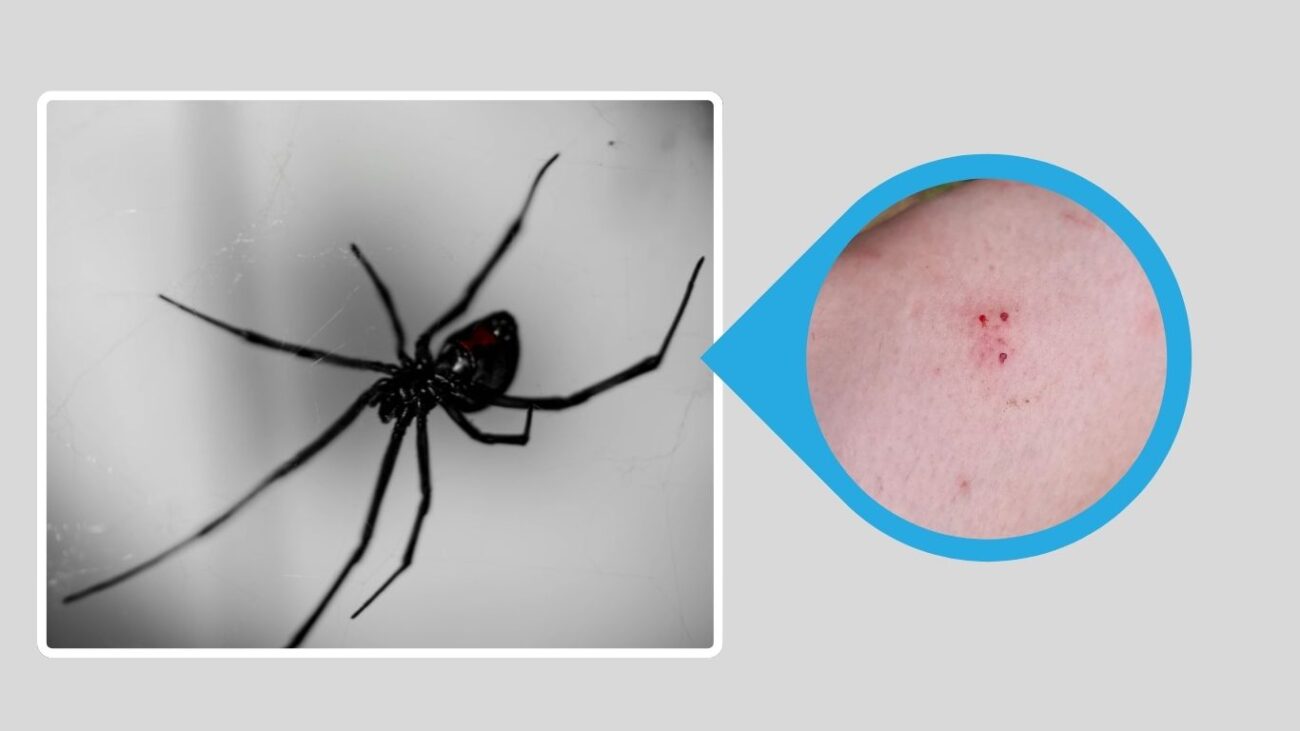

The Indian Black Widow is native to the Indian subcontinent and parts of Southeast Asia. It is considered one of the most venomous spiders in the region and plays an important role in controlling insect populations. Although rarely encountered by people, bites have been documented in agricultural and rural settings.
Identification
- Deep black or dark brown body
- Faint or broken red or orange hourglass on the underside
- Abdomen may feature subtle white or red side spots
- Females grow larger than males and appear more robust
- Males are much smaller, with less vivid coloring
Habitat
This species typically inhabits dry, arid zones, abandoned termite mounds, rock crevices, and brick piles. In villages and rural homes, they may be found in storerooms, barns, and unused corners of buildings. Their tangled webs are built close to the ground and often hidden among clutter or stones.
Bite
The bite of the Indian Black Widow is medically significant. Victims may experience intense burning pain at the bite site within 20–40 minutes, followed by muscle cramps, sweating, nausea, and sometimes difficulty breathing. Hospital care is essential in severe cases, especially for children, elderly, or individuals with existing health issues.
What regions are Indian Black Widows found in?
They are found throughout India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and some regions of Nepal and Sri Lanka.
Are Indian Black Widow bites common?
No, they are rare and usually occur when the spider is disturbed during cleaning, farming, or moving stored items in dark spaces.
What’s the best way to avoid a bite?
Always use gloves and a stick when handling firewood, moving rocks, or cleaning rarely used corners. Shake out stored clothes or shoes before wearing.
10. Middle Eastern Black Widow (Latrodectus renivulvatus)
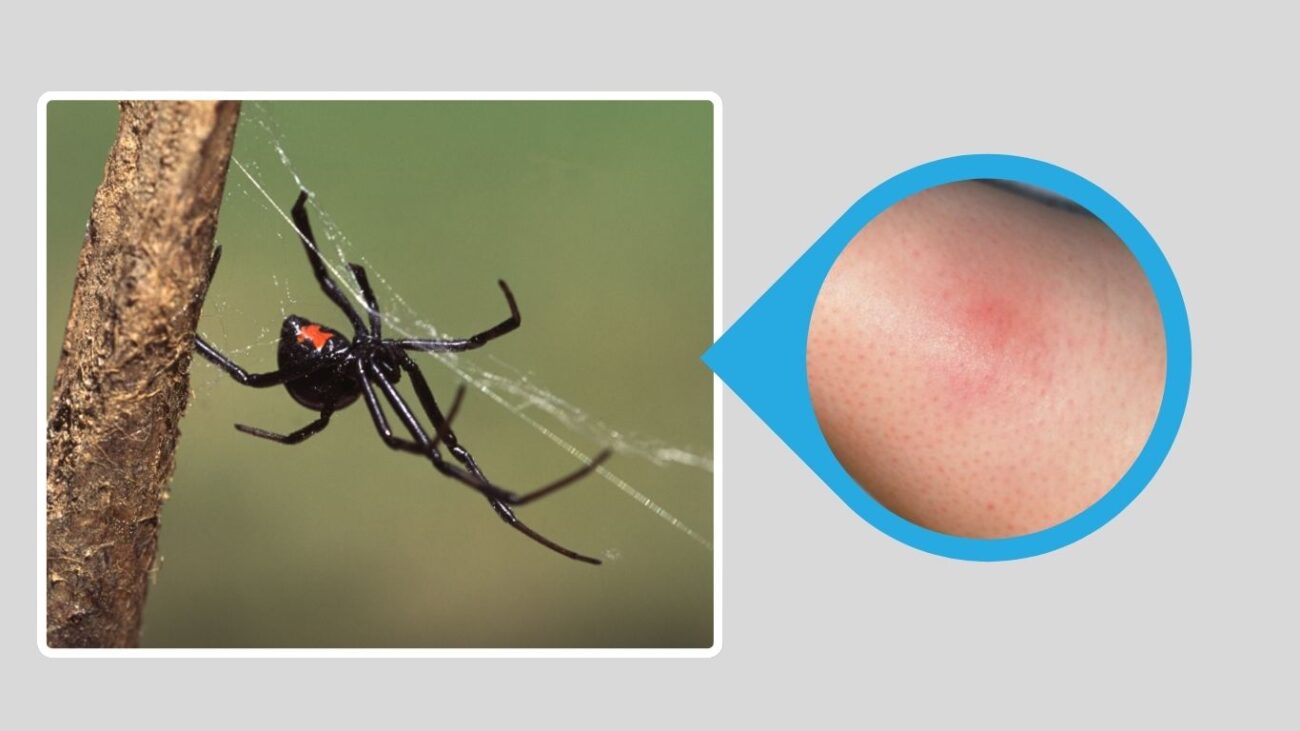

The Middle Eastern Black Widow is distributed across arid and semi-arid regions of the Middle East, including Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and surrounding countries. It is a medically important species known for its neurotoxic venom and hidden, ground-level habitats.
Identification
- Glossy black body
- Hourglass shape may be red, orange, or pale and often incomplete
- Rounded abdomen with possible faint side markings
- Females significantly larger than males
- Males smaller, brownish, and less visible
Habitat
This species prefers dry desert regions, rocky slopes, and open shrublands. It hides in cracks, under stones, within abandoned rodent burrows, or along the foundations of structures. In human settlements, they may be found in basements, unused corners of homes, or storage sheds. They weave irregular webs close to the ground and often remain hidden until provoked.
Bite
The venom causes latrodectism—a condition marked by severe pain, muscle spasms, fever, and nausea. Bites are particularly dangerous to the elderly and individuals with heart conditions. Although fatalities are rare, the symptoms may persist for days and require supportive care, especially intravenous fluids and muscle relaxants in severe cases.
Where are these spiders most commonly found?
They are mainly found in desert landscapes and dry regions of the Middle East, especially around human settlements with access to shelter.
Are they a public health concern in their native region?
Yes, especially in rural and remote areas where access to medical care is limited. Public awareness is increasing in endemic zones.
How can bites be prevented?
Avoid reaching into dark crevices, wear gloves when working outdoors, and seal gaps around buildings to keep them out.
11. White Widow (Latrodectus pallidus)

The White Widow is one of the lesser-known members of the widow spider family. Native to parts of Eastern Europe and Central Asia, it gets its name from its pale, almost creamy or white coloring. Though less dramatic in appearance, it still delivers venom similar to that of other Latrodectus species.
Identification
- Pale beige to creamy white body
- Hourglass marking may be light yellow or nearly invisible
- Abdomen smooth and oval-shaped
- Females appear larger and more bulbous
- Males are smaller and rarely seen
Habitat
White Widows are found in semi-arid and steppe environments, particularly in countries like Russia, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan. They tend to build webs in dry grasslands, under flat rocks, in old buildings, and sometimes even in residential foundations or storage areas. They prefer isolated, dry, and hidden environments.
Bite
While their venom is similar in potency to other black widow species, bites are less frequently reported. When bites do occur, they may result in muscle cramps, chest tightness, sweating, and anxiety-like symptoms. Recovery is typically quick with supportive care, but medical help should still be sought.
Why is it called a “White Widow”?
The name comes from its unusually pale or light coloration, which contrasts with the typical black appearance of most widow spiders.
Is the bite of a White Widow dangerous?
Yes, it can be, especially for vulnerable individuals, though it’s generally less likely to result in serious complications than other widow species.
Are White Widows active during the day or night?
They are nocturnal, staying hidden during the day and becoming active at night to repair webs or capture prey.
12. Malagasy Widow (Latrodectus menavodi)

The Malagasy Widow is endemic to Madagascar and some nearby islands in the Indian Ocean. This species is lesser-known globally but plays a role in the ecological balance of its native regions. Like other widow spiders, it carries potent neurotoxic venom.
Identification
- Jet black or very dark brown body
- Hourglass marking may be faded, orange, or absent
- Some individuals show red or white dots on the abdomen
- Females are large and visibly rounded
- Males are tiny, lighter in color, and rarely seen
Habitat
Found mostly in the dry forests, grassy plains, and rural settlements of Madagascar. They build irregular webs near the ground, often under rocks, dry leaves, or near tree bases. In human-influenced areas, they may settle around homes, in crevices, or under unused equipment.
Bite
The venom can cause intense local pain, dizziness, muscle stiffness, and abdominal discomfort. Although there are no widespread records of fatal bites, symptoms can be severe without proper care. Due to limited medical access in rural parts of Madagascar, awareness and prevention are important.
Are Malagasy Widows commonly seen in urban areas?
They are more common in rural and semi-rural zones but may enter villages, especially around outdoor structures or wood storage.
What should you do if bitten in a remote location?
Clean the wound, stay calm, limit movement, and get to a healthcare center as soon as possible. Pain relief and hydration are crucial.
How do locals usually avoid them?
By checking dark corners, using gloves for yard work, and shaking out stored items like shoes or bags before use.
13. Karoo Widow (Latrodectus karrooensis)

Native to the arid Karoo region of South Africa, the Karoo Widow is adapted to harsh, dry climates and is part of the African widow spider group. Its venom is medically significant and similar to other black widow species.
Identification
- Glossy black or dark brown body
- Hourglass may be red, orange, or faint and broken
- Abdomen may have lateral red streaks
- Females are noticeably larger than males
- Males are light brown and less distinct
Habitat
Karoo Widows prefer scrubland, desert brush, and rocky outcrops. They are commonly found under loose stones, inside rock walls, and in dry drainage ditches. In some cases, they may enter farm buildings or garden sheds in search of prey or shelter.
Bite
The venom produces symptoms similar to other Latrodectus bites: muscle cramps, lower back pain, sweating, and restlessness. Symptoms generally develop within an hour and may last for a day or more. While not often life-threatening, medical attention is recommended for strong reactions.
Is the Karoo Widow dangerous to livestock or pets?
Pets and small animals may be at risk if bitten. Livestock are rarely affected unless confined with infested materials.
How do they survive in dry climates?
They are adapted to conserve moisture, build webs in shaded crevices, and hunt mainly at night when temperatures drop.
What is the best treatment for a bite in remote Karoo areas?
Use cold compresses, stay hydrated, and seek help from local health clinics. In severe cases, antivenom may be needed.
14. Zimbabwean Widow (Latrodectus rhodesiensis)

The Zimbabwean Widow is found primarily in Zimbabwe and neighboring regions of southern Africa. It is a close relative of other African widow species and carries potent venom capable of causing serious symptoms in humans. Despite its fearsome bite, this spider tends to avoid human contact.
Identification
- Dark black or brown body
- Hourglass marking is often orange to red, but may appear broken
- Females have a full, rounded abdomen with faint side markings
- Males are much smaller and lighter in color
- Abdomen surface smooth and slightly reflective
Habitat
Latrodectus rhodesiensis lives in savannas, dry forest edges, and near human dwellings in rural areas. They often make webs under stone slabs, in garden walls, hollow logs, or even within gaps of outdoor furniture and tools. These spiders are especially active at night and prefer dry, warm areas.
Bite
Bites typically produce symptoms such as sharp pain, localized swelling, muscle cramps, sweating, and anxiety. In serious cases, nausea, headache, and hypertension can occur. Hospitalization may be necessary for those with severe reactions, especially children and older adults.
How do Zimbabwean Widows interact with humans?
They generally avoid humans and bite only when provoked or accidentally pressed against the skin.
What time of year are bites most common?
Bites are more frequent during hot months when the spiders are most active and when people are working outside or handling materials stored outdoors.
Can these spiders be found in homes?
Yes, especially in rural homes or structures with cracks, clutter, or unsealed access to outdoor areas.
15. Desert Widow (Latrodectus revivensis)

The Desert Widow is native to arid regions of the Middle East, including Israel, Egypt, and parts of Jordan. It has adapted to extreme desert conditions and is most often found in remote, sandy, and rocky locations. Though not aggressive, its bite is dangerous due to potent venom.
Identification
- Shiny black body with reddish-orange hourglass
- Hourglass may be narrow and slightly faded
- Abdomen rounded, sometimes with faint side spots
- Females larger and more visible
- Males smaller and usually lighter in color
Habitat
Desert Widows are specialized for life in harsh, dry climates. They inhabit sandy dunes, dry rock piles, abandoned burrows, and under desert vegetation. In human-modified environments, they may occupy cracks in walls, irrigation equipment, or under old machinery. Their webs are sparse and spread close to the ground, often hidden beneath cover.
Bite
The venom is potent and can lead to severe pain, cramps, chills, and sweating. In hot desert climates, dehydration from symptoms may worsen the condition. Though rarely fatal, the bite should be treated promptly to prevent complications.
How do Desert Widows survive extreme temperatures?
They shelter in shaded crevices, stay inactive during the heat of the day, and become active at night to hunt.
Are bites from Desert Widows common?
They are rare due to the spider’s remote habitat and nocturnal habits, but do occur when people disturb their hiding spots.
What’s the recommended first aid in desert areas?
Stay calm, avoid physical exertion, hydrate, apply a cold compress, and seek the nearest medical facility immediately.